4th March, 2023
In Android, ImageView is a view used to display images. We can set the image to the ImageView using the android:src attribute. Let’s take an overview of Android ImageView.
1. Add ImageView in Android App
We can create/add Android ImageView in two ways:
1.1 Create/Add ImageView in XML layout file
Open the xml layout designer in Android studio and select the ImageView from the palette, add it to the layout.
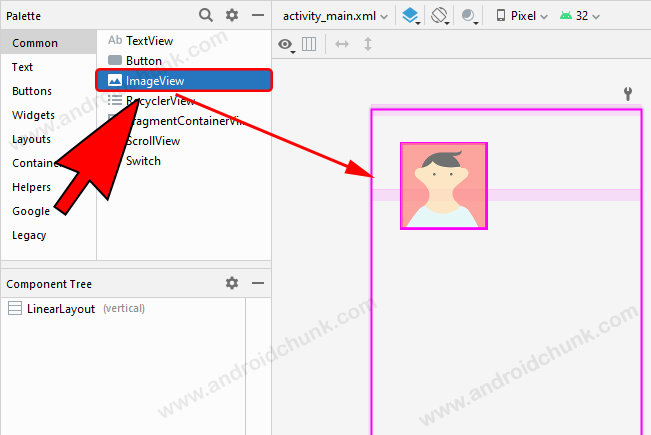
Android studio will ask you to select a resource for ImageView. Pick a resource and click the OK button.
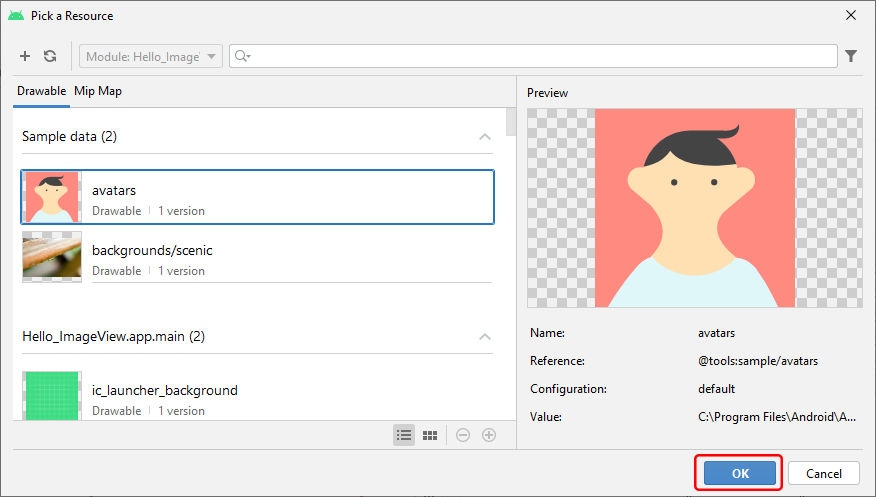
Done! The ImageView has been successfully added to the XML layout file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" />
</LinearLayout>
We can also add our resources by clicking the + icon located at the corner.
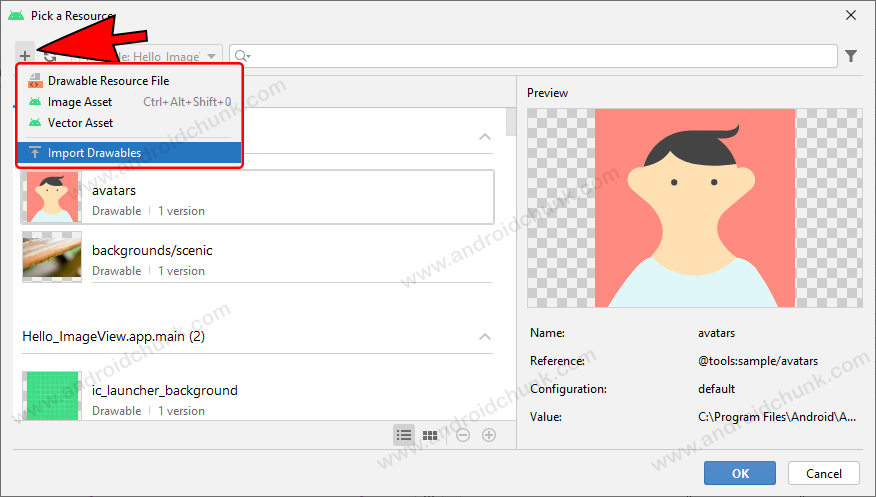
1.2 Create ImageView Programmatically in Android
Alternatively, we can create/add Android ImageView programmatically using Kotlin/Java code. See the code below.
package com.androidchunk.helloimageview
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.ImageView
import android.widget.LinearLayout
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val linearLayout = findViewById<LinearLayout>(R.id.linearlayout12)
//create a imageView
val imageView = ImageView(this)
//set image resource
imageView.setImageResource(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
//add imageView to the layout
linearLayout.addView(imageView)
}
}
package com.androidchunk.helloimageview;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout linearLayout = findViewById(R.id.linearlayout12);
//create a imageView
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(this);
//set image resource
imageView.setImageResource(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//add imageView to the layout
linearLayout.addView(imageView);
}
}
2. Scale Types of Android ImageView
In Android, The ScaleType attribute is used to uniformly scaling the bounds of the imageView. ImageView can display image based on the ScaleType attribute. Below is the list of ScaleType of Android ImageView with preview.
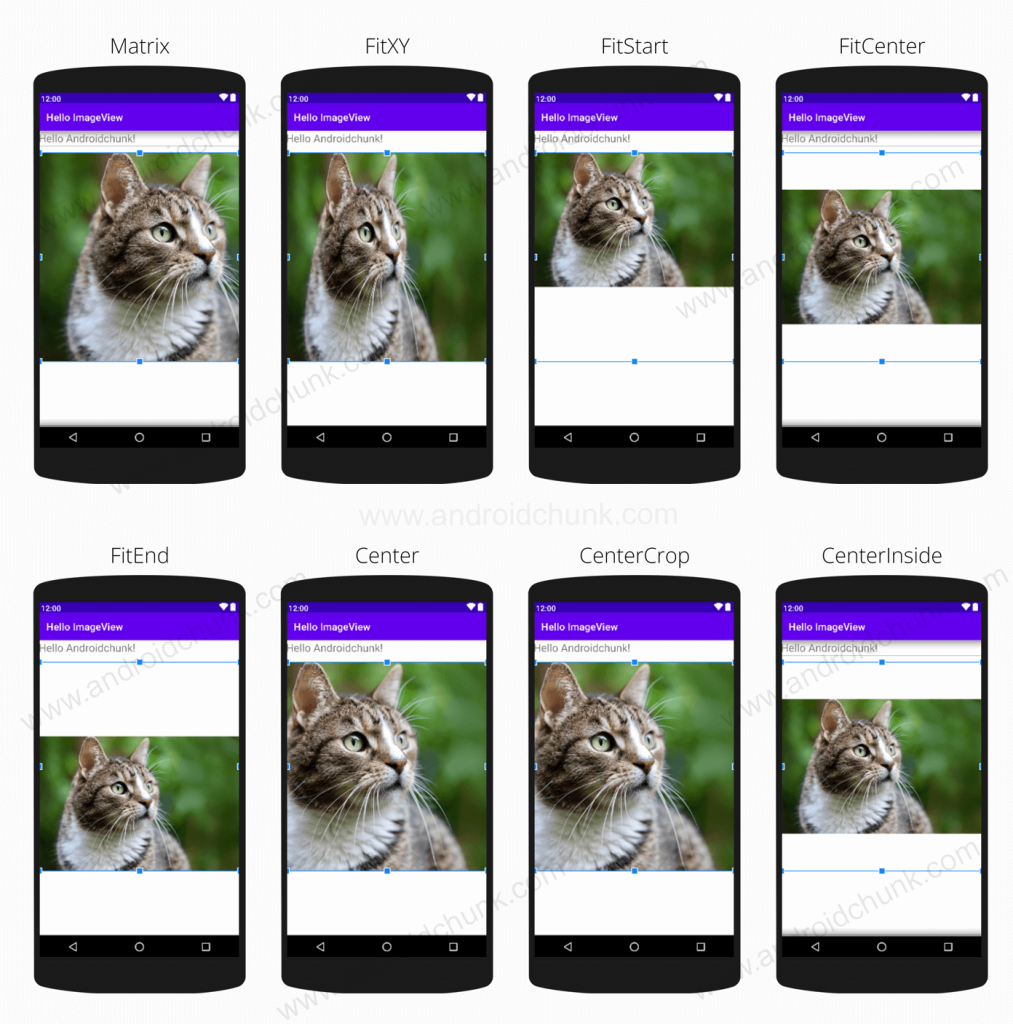
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| matrix | It is used to scale the image using a supplied Matrix class. |
| fitXY | It scales the x and y dimensions to exactly match the view size. Not maintain the image aspect ratio |
| fitStart | It scales the image from the start of the container. |
| fitCenter | It scales the image from the center. It also maintain the aspect ratio of the Image. |
| fitEnd | It scales the image from the end of the container. |
| center | It centers the image within the ImageView. It does not scale the image. |
| centerCrop | It scales the image uniformly. It maintains the aspect ratio of the image to make it equal or larger than the dimensions of the image view; Centers the image within the imageView |
| centerInside | It scales the image to fit inside the view, maintaining the aspect ratio of the image. It does not match the image edge to the edge of the view. |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello Androidchunk!"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:scaleType="matrix"
android:src="@drawable/cat_7535" />
</LinearLayout>
5. Android ImageView Example
Let’s take an example in which we will use Android ImageView.
Step 5.1: Create New Project
Create a new project in Android Studio from File ⇒ New Project and select Empty Activity from the templates.
Step 5.2: Enable View Binding
In this example we are using Android Jetpack’s feature view binding.
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.android'
}
android {
...
...
buildFeatures {
viewBinding = true
}
...
...
}
dependencies {
...
...
...
}
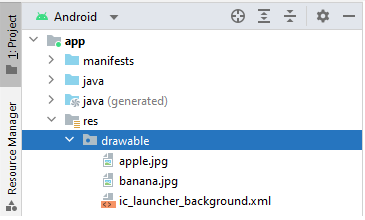
Step 5.3: Add Resource Images
Expand the res folder and add the following images to the drawable folder.
Step 5.4: Add ImageView to the XML Layout (UI)
Open the xml layout file and add a ImageView from the palette. See the code below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello Androidchunk!"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/bananaImageView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:src="@drawable/banana" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/appleImageView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:src="@drawable/apple" />
</LinearLayout>
Step 5.5: Update Activity File
Open the activity file and add a click listener to the ImageView. We will display a toast when the imageview is clicked. Run the app and check the output.
package com.androidchunk.helloimageview
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.androidchunk.helloimageview.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
//view binding
lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.getRoot())
//banana image click listener
binding.bananaImageView.setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(
this@MainActivity,
"You clicked on the banana image",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
})
//apple image click listener
binding.appleImageView.setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(
this@MainActivity,
"You clicked on the apple image",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
})
}
}
package com.androidchunk.helloimageview;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.androidchunk.helloimageview.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;
class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//view binding
private ActivityMainBinding binding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
setContentView(binding.getRoot());
//banana image click listener
binding.bananaImageView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "You clicked on the banana image", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
//apple image click listener
binding.appleImageView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "You clicked on the apple image", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
Step 5.6: Output
Happy coding!



